
Limited UEFI boot support was included with Win7. Windows XP (64 bit only), Windows Vista (32 & 64 bit) and Windows 2k3 SP1 and later support GPT (non-boot disks only). This is known as Secure Boot and provides protection from an entire class of malware. UEFI enables Microsoft to include signed boot loader checks. This prevents applications that may not be ‘GPT aware’ (created before the EFI standard) from accidentally overwriting the GPT partitions. Sector 0, by convention, contains a (protective) MBR configured with a single partition spanning the entire disk.
This partition will be mounted as part of the EFI boot process it will contain EFI boot code and configuration data specific for the installed OS and CPU ISA. A type is reserved for a FAT32 formatted (EFI system partition). The G in GPT references the two GUIDs used to uniquely identify each partition and its type. This led to GUID Partition Table (GPT) was introduced as part of the Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) standard, for use with UEFI-based systems.įeatures include support for 9.4 ZB disks, 128 partitions, checksum protection with a backup table maintained at the back of the disk in case of a checksum failure of the primary table. When the ill fated Itanium was introduced, Intel needed a new boot scheme (due to the limitations of BIOS mentioned above). BIOS is only compatible with x86 compatible CPUs. This and the sector at a time disk i/o results in a very slow first stage boot process. If you install 64Bit Windows on a BIOS booting system, the first stage of the boot process will require the CPU to operate in an 8086 compatible mode ( ). It is intimately associated with the real mode x86 instruction set. The associated booting scheme is known as BIOS (also known as legacy by EFI firmware). The MBR scheme can only address 2TB of storage and supports a maximum of 4 bootable partitions. There is also a flag to indicate which partition contains the files required to continue the boot process. Each table entry contains the location of the partition and the partition (filesystem) type.

This sector contains the partition table and executable code used to bootstrap the loading of the Operating System.

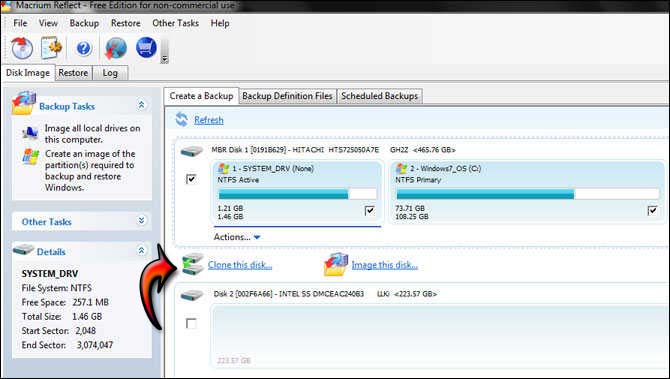
MBR refers directly to a special boot sector located at the very beginning of a mass storage device. The older of the two partitioning schemes is Master Boot Record (MBR). There are many schemes to partition a disk, however MBR and GPT are the two found on hardware platforms running Windows. Partitions typically contain filesystems. The partitioning scheme chosen also defines the boot mechanism. To enable multiple volumes to exist on one storage device, it is divided into partitions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
